denominator
200000
39 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Update frequencies
-
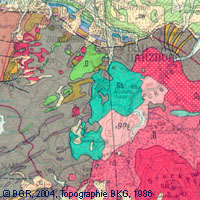
The map series General Geological Map of the Federal Republic of Germany 1:200,000 (GÜK200) is the result of cooperation between the State Geological Surveys of the Federal Republic of Germany (SGD), the Geological Surveys of neighbouring countries and the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR). The GÜK200 displays the surface geology of Germany and adjacent areas of neighbouring countries on 55 map sheets. The map sheets show the regional dissemination of more than 3800 geological units. The geological units contain information on stratigraphy (age), genesis and petrography (composition) of the rocks. Each printed/scanned map sheet contains one or several geological cross-sections which give an insight into the subsurface. The digital data of the map series are stored separately for each map sheet. According to this geological units/polygons, their boundaries, tectonic linear elements and, if present, ice sheet boundaries are saved as a discrete layer in a shapefile for the single map sheets. The attributes of the geological units contain information – like in the printed map sheets – on stratigraphy, genesis and petrography of the rocks.
-
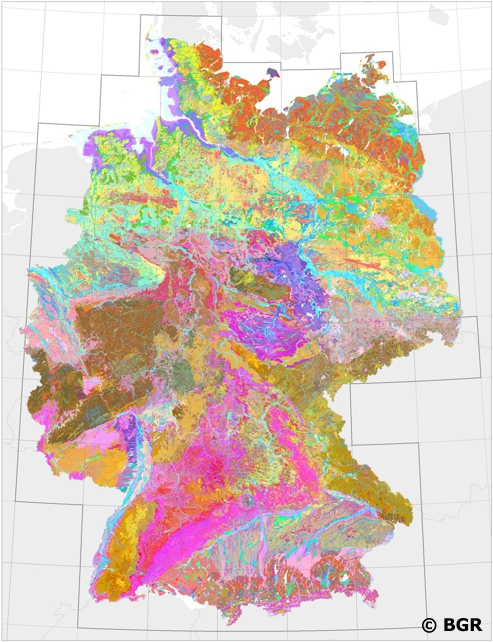
Nation-wide land use strategies and planning as well as soil protection require harmonised and standardised area-covering information. Such data is provided by the digital Soil Map of Germany at scale 1:200,000 (BUEK200). The pedological data of this map, stored in a relational database, is used to demonstrate the abundance and the associations of soils and their basic properties in Germany. However, the main purpose of the BUEK200 is to offer a database which allows the estimation and visualisation of soil functions, soil potentials and soil hazards. To achieve comparable soil information throughout Germany the BGR and the soil surveys of the federal lands have elaborated and defined BUEK200 standards concerning the map (e.g. delineation and description of mapping units) and its database (e.g. database model, parameters, codification).
-
Der Datensatz zeigt die Tiefenlage des Top bzw. der Oberkante tiefliegender Aquifere des Leinekarbonates in Thüringen.
-
Der Datensatz zeigt die Mächtigkeiten für tiefliegende Aquifere des Staßfurtkarbonates (Hauptdolomit in Randwallausbildung) in Thüringen.
-

Als besondere Landschaftsräume dienen Naturparke (NRP) sowohl dem Erhalt einmaliger Kulturlandschaften als auch deren touristischen Vermarktung zu Zwecken der Erholung und Bildung. Der Erhalt der Biotop- und Artenvielfalt wird über großräumige Landschafts- und Naturschutzgebiete gewährleistet. Rechtliche Grundlage ist dabei § 27 Abs. des 1 BNatSchG, das die einheitliche Entwicklung und Pflege der entsprechenden Gebiete vorsieht.
-
Der Datensatz zeigt die Temperaturverteilung für tiefliegende Aquifere des Mittleren Buntsandsteins in Thüringen.
-
Der Datensatz zeigt die Mächtigkeiten für tiefliegende Aquifere des Leinekarbonates in Thüringen.
-
digitale Umsetzung des Kartenwerkes Geologische Karte von Mecklenburg-Vorpommern Karte der quartären Bildungen - Oberfläche bis fünf Meter Tiefe vorhanden: ca. 90% der Landesfläche Blatt Bad/Doberan Rostock, 1995 Blatt Stralsund, 1996 Blatt Güstrow, 1995 Blatt Boizenburg/Schwerin, 2002 Blatt Neubrandenburg/Torgelow, 2003
-
Der Datensatz zeigt die Temperaturverteilung für tiefliegende Aquifere des Staßfurtkarbonates (Hauptdolomit in Randwallausbildung) in Thüringen.
-
Der Datensatz zeigt die Mächtigkeiten für tiefliegende Aquifere des Werrakarbonates (Werradolomit- und Riff-Fazies) in Thüringen.
 INSPIRE-1
INSPIRE-1