Format
Filegeodatabase
1 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
-
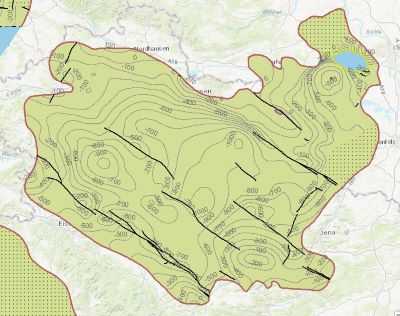
Which salt formations are suitable for storing hydrogen or compressed air? In the InSpEE-DS research project, scientists developed requirements and criteria for the assessment of suitable sites even if their exploration is still at an early stage and there is little knowledge of the salinaries’ structures. Scientists at DEEP.KBB GmbH in Hanover, worked together with their project partners at the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources and the Leibniz University Hanover, Institute for Geotechnics Hanover, to develop the planning basis for the site selection and for the construction of storage caverns in flat layered salt and multiple or double saliniferous formations. Such caverns could store renewable energy in the form of hydrogen or compressed air. While the previous project InSpEE was limited to salt formations of great thickness in Northern Germany, salt horizons of different ages have now been examined all over Germany. To estimate the potential, depth contour maps of the top and the base as well as thickness maps of the respective stratigraphic units and reference profiles were developed. Information on compressed air and hydrogen storage potential were given for the identified areas and for the individual federal states. The web service "Information system for flat layered salt" gives access to this data. The scale of display is limited to a minimum of 1:300.000. This geographic information is product of a BMWi-funded research project "InSpEE-DS" running from the year 2015 to 2019. The acronym stands for "Information system salt: planning basis, selection criteria and estimation of the potential for the construction of salt caverns for the storage of renewable energies (hydrogen and compressed air) - double saline and flat salt layers".
 INSPIRE-1
INSPIRE-1